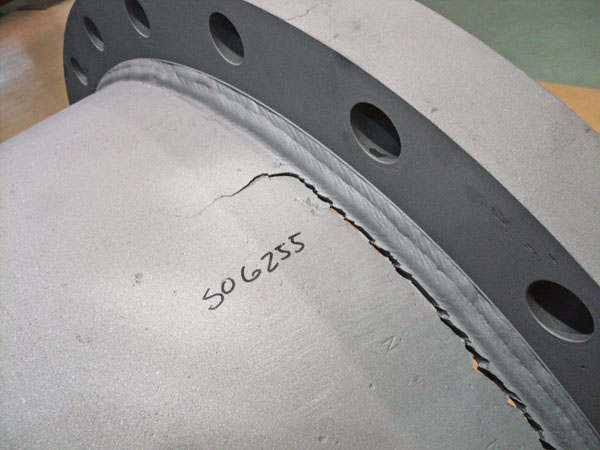
Design flaws cause catastrophic failure in a geothermal power station hotwell in New Zealand.
Written by: Chandra Verma (Hydro, Inc.)
Publisher: Pumps & Systems / August 2016
Despite well-documented pump system standards and basic requirements, omission of certain crucial design steps remains a problem in the industry, often causing disastrous outcomes for the end user. When suppliers, manufacturers and/or contractors take shortcuts, technical and commercial risk can present serious ramifications for a large project.Communication failures between the end user’s staff, suppliers and contractors can intensify problems, especially when pumps that may not be appropriate for a given job are commissioned and put into service. Without the end user’s knowledge, a facility may install pumps that have not been properly tested for the application, were fabricated to inferior standards or subject to other shortcuts that adversely affect performance.Sometimes the end user becomes aware of shortcut-derived flaws during the commissioning stage. Other times, problems in equipment or system design might not be evident immediately—they surface during subsequent plant and equipment maintenance that reveals potentially dangerous, hidden conditions. The ensuing problems can lead to tense project politics and expensive rectification, including hiring independent consultants.
Suppliers, manufacturers and contractors take shortcuts for various reasons. These shortcuts can be attributed to a lack of experience with how a pump might be deployed in the field. There may be miscommunication of technical details from both the user and supplier or between the user and contractor.
Budget constraints and concerns can also result in omissions; commercial reality can cause a manufacturer or supplier to make a project’s bottom line cheaper by reducing the cost of equipment and cutting corners.
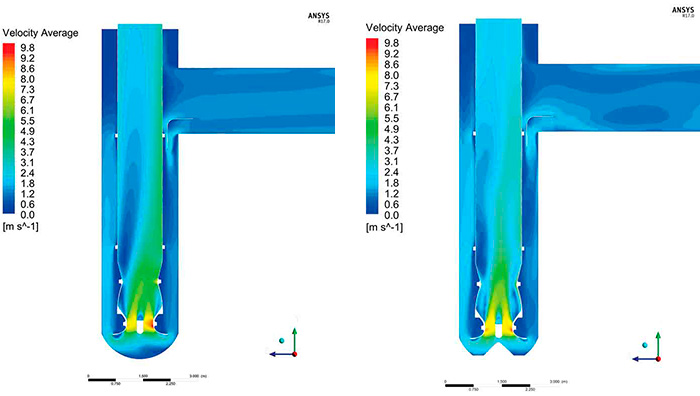
Figure 1. The velocity distribution of the original (left) and modified geometries (right)
Continue reading →





