A Case Study in Diagnostic Testing and Innovative Solutions
Some services are inherently difficult due to factors such as fluid quality or multiple disparate operating points. These factors are an inherent part of the process and cannot be changed to improve reliability. Harsh applications can be a costly prospect, both in overhaul costs and in the time and labor required for frequent servicing. Many times we become caught in the perception that there is no improvement to be had for these services. A short mean-time-between-failures (MTBF) becomes routine and expected, and maintenance activities and parts procurement are built around this expectation.
When equipment is sent out for refurbishment, the expectation is that mechanical and hydraulic performance upon reinstallation will be better than what was experienced in the worn condition. This assumption holds true in most cases; however, sometimes unexpected behavior can occur after a pump is remanufactured and reinstalled. While it is easy to jump to the conclusion that these performance changes were caused by errors made during the repair or installation of the equipment, sometimes the problem is more complex and related to latent weaknesses in the design that had lain dormant until refurbishment.
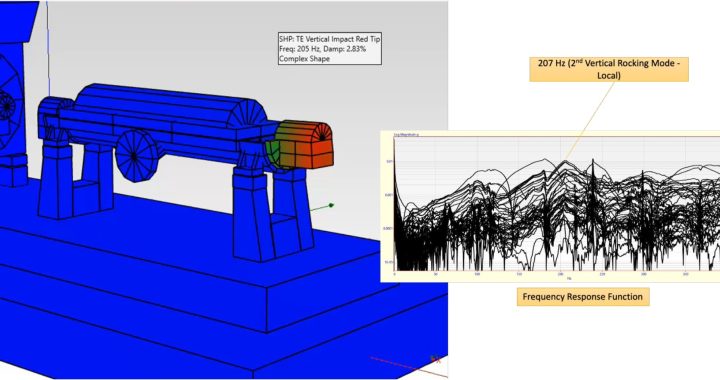
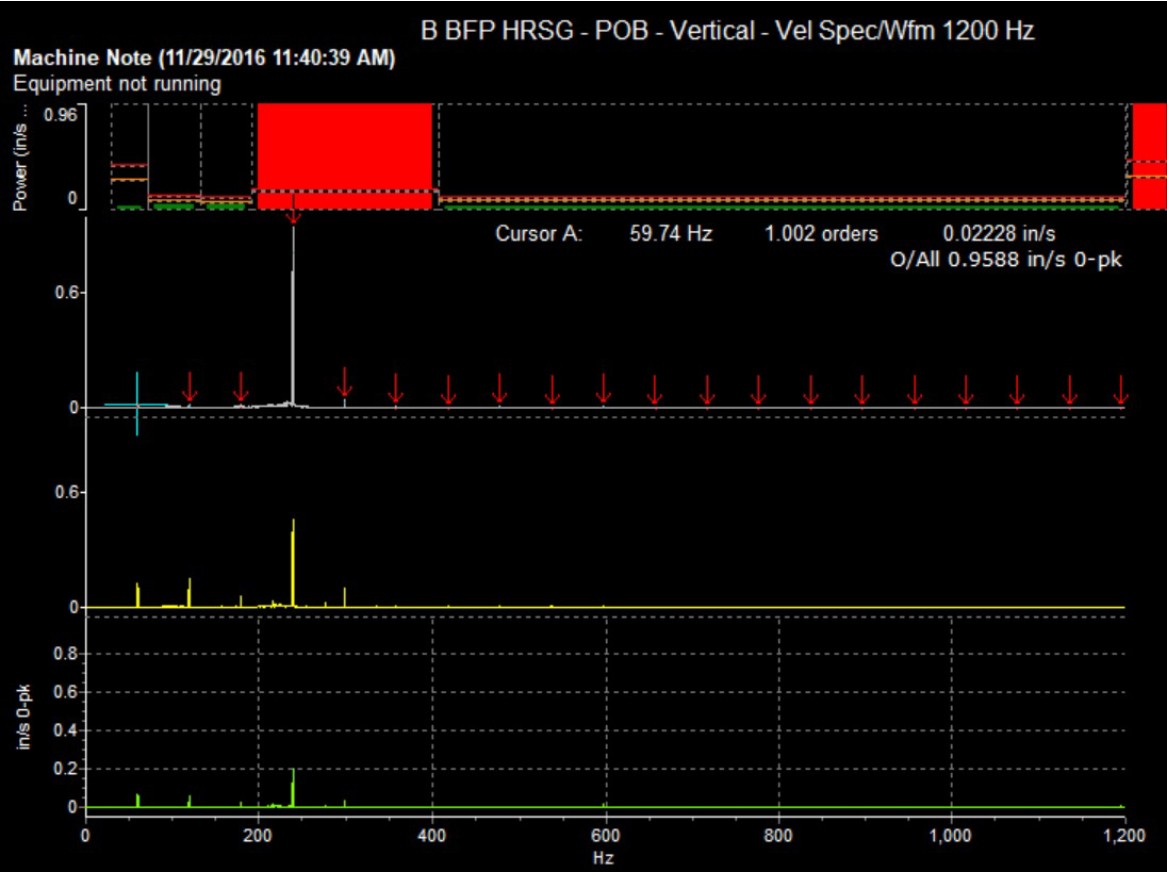
This scenario was experienced by a power utility in the Southeastern US when they ran into significant vibration increases after one of their boiler feed pumps was refurbished by a local repair shop. Concerned by the level of vibration, the utility reached out to Hydro South, who have extensive experience in this application and model. From there, Hydro Reliability Services was called on to collect data on the problematic equipment and use advanced modeling tools to understand the nature of the vibration. The field testing and analysis revealed that pump had been operating with a very small margin between a structural resonance and one of the pump forcing frequencies. Armed with this information, solutions were developed to increase this margin and return to stable operation.
Read the full case study in Pumps & Systems March 2024 edition.
Learn more about Hydro Reliability Services and how they support field testing, vibration troubleshooting, and advanced system studies.