Careful analysis identified the issue with this multistage, oil transfer pump.
This case study describes the method used to solve the high bearing temperature problem and outlines the flow physics that contributed to the high thrust bearing temperature. The customer contacted an engineering services company after the original pump manufacturer failed to remedy the problem.
The company’s forensic approach to this problem involved two distinct methodologies:
- Diligent and in-depth analysis of site data relating to the problem
- Rigorous scrutiny and analysis of the pump geometry and build against the background
The engineering services company identified several scenarios that could cause this temperature rise, then narrowed down the list to establish a root cause.
Site Data Analysis
The behavior of thrust bearing pads during startup is seldom investigated. The temperature rise of the pads can be attributed to two distinct causes—thrust developed during startup and environmental and oil conditions (see Figure 1).
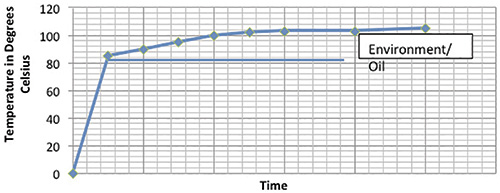
Figure 1. Behavior of thrust bearing pads based on thrust and environmental conditions (Article images and graphics courtesy of Hydro Inc.)
Based on comparisons with previous site data, both the thrust and oil cooling had altered. Analysis of the temperature data at the motor bearings, which were experiencing oil temperature increases of 10 to 15 C, further supported the conclusion. Continue reading
