Introduction:
Maintaining the reliability and efficiency of critical equipment is paramount. This case study highlights the value of continuous, real-time condition monitoring by describing the how a premature failure was identified and resolved in a blower unit installed at a specialty materials manufacturer. The proactive implementation of Hydro’s Centaur condition monitoring played a pivotal role in early detection, enabling swift intervention and preventing unnecessary downtime.
Background:
A large US chemical plant that creates a variety of specialty materials had ongoing troubles with the centrifugal blowers in their PVC division. The units are critical to production and do not have spare backup units. Hydro’s Centaur condition monitoring solution was deployed on these blowers to understand the nature of the failures as well provide insight into when the units needed attention. One of the blower units began exhibiting concerning signs on January 04, 2024. Vibration levels steadily increased over the subsequent weeks, reaching a critical point on February 9th, 2024. This prompted the decision to shut down the unit and perform a root cause analysis to quickly determine remedial actions and keep production downtime to a minimum.
Events and Details:
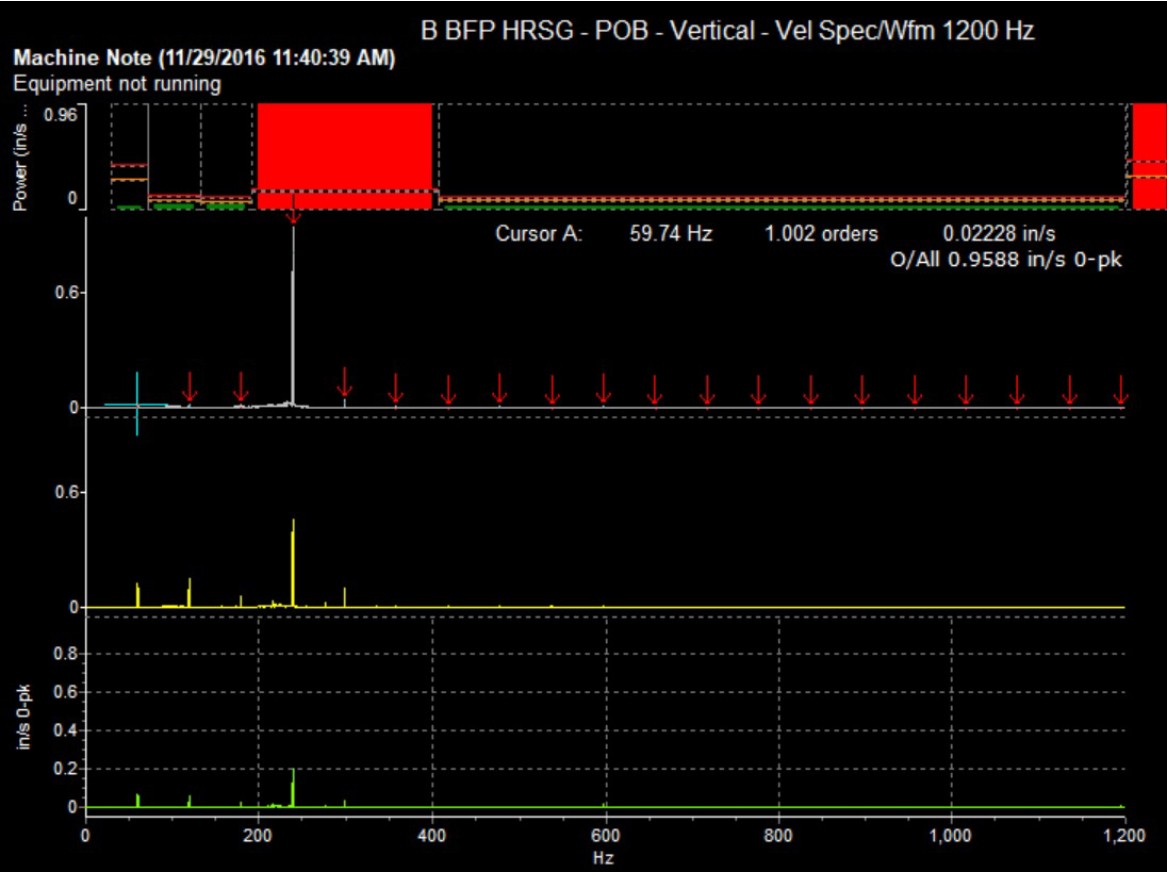
When elevated vibration amplitudes were first detected on the problematic blower, they were in the Blower Outboard Bearing in the vertical direction (BOBV). The velocity amplitude shown below crossed the warning threshold on January 06, 2024, alerting both Hydro and the end user’s site engineers that a condition was present and in blower was in the early stages of degradation. The observation was discussed during the weekly touchpoint between Hydro and the plant, where Hydro would review the health of all monitored assets and address any alarm events captured using Centaur with site stakeholders.
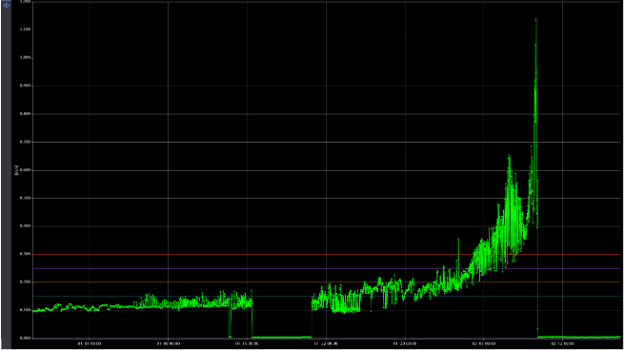
Figure 1: Velocity Amplitude as Several Alarm Thresholds Breached
The vibration velocity amplitudes continued to climb, and on January 25, 2024 they crossed the Alarm #1 threshold. The Alarm #2 threshold was breached on February 01, 2024. Continual touchpoint meetings highlighted the worsening conditions and provided an analysis of the suspected failure mode(s) affecting the blower mechanical condition. The below multi-spectrum chart shows the spectra at the BOBV location at various points along the trend – mapping the signature of the degradation.
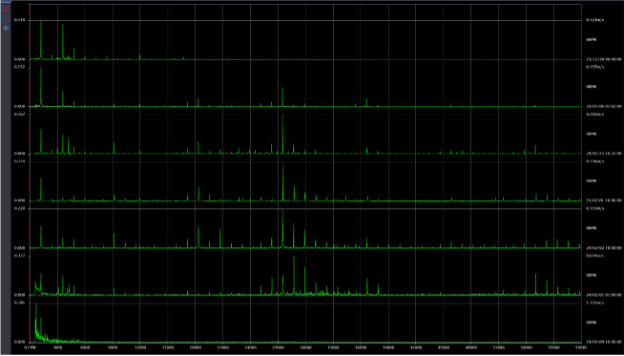
Figure 2: Multi-Spectrum Chart of BOBV Location
The chart starts with the spectra during “normal” conditions, prior to the observed degradation. Peaks at 1X and several harmonics are present with an amplitude less than 0.15 ips RMS. As the problem is observed and continues to worsen, bearing fault frequencies and harmonic excitation appear and continue to get worse. The lowest spectrum in the chart shows vibration velocity amplitude during the final sample, when it is greater than 1 ips RMS – very severe. At this point, all the energy has moved to 1X or less than 1X frequencies – a common occurrence when a failure mode is in its final stages.
The following two spectra charts take a closer look at the condition, one chart showing the initial conditions prior to degradation and the other closer to the end of operation where bearing fault frequencies and harmonic excitation can be detected.
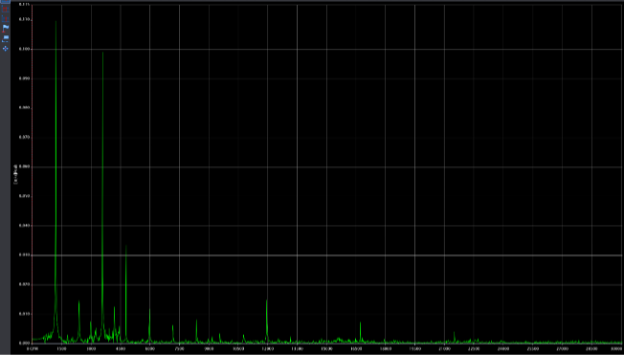
Figure 3: Initial Conditions
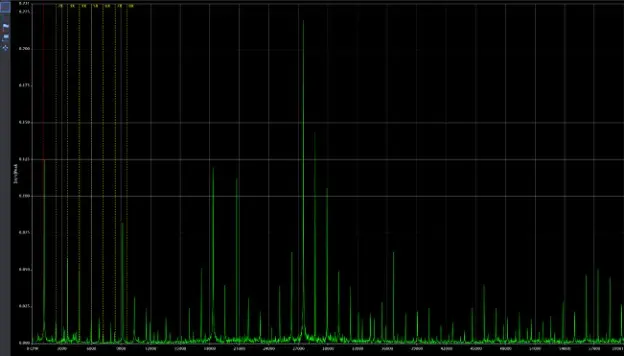
Figure 4: Near End of Operation
In parallel with the velocity measurement, Hydro and the plant reliability engineers reviewed the acceleration measurements at the same location. Acceleration often leads to velocity readings, particularly for bearing failure. The chart below shows the trend for acceleration with the amplitude shown in g’s.
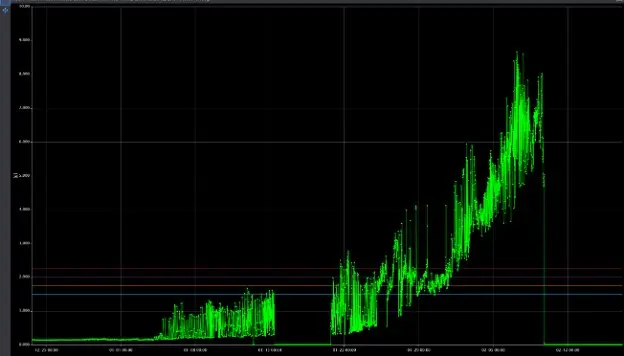
Figure 5: Acceleration Trend
The following four charts show the spectra and waveform data for acceleration readings at two points during the degradation period. The first two charts show the early stages of failure with peak-to-peak amplitudes of ~6 g’s and harmonic excitation in the spectrum. The second two show acceleration data at a later stage of degradation with peak-to-peak amplitudes at ~30 g’s and increased discrete frequency amplitudes in the spectrum.
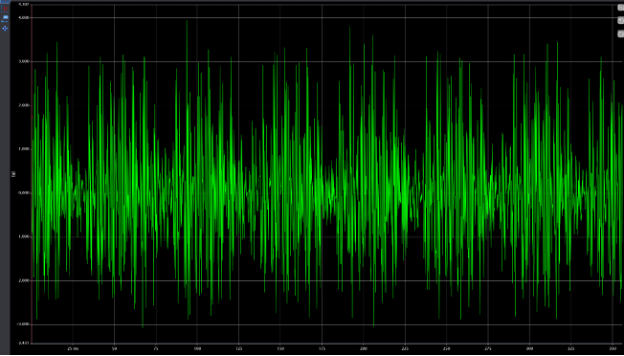
Figure 6: Waveform- Early Stage of Failure
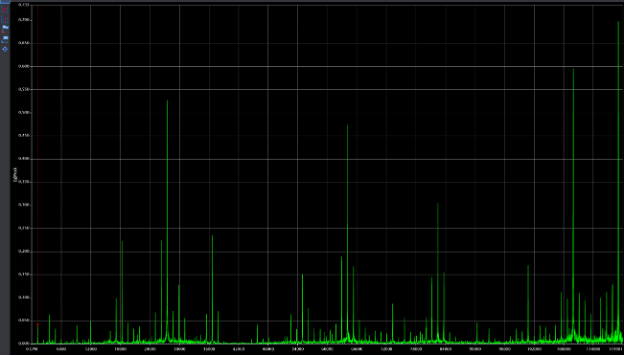
Figure 7: Spectrum- Early Stages of Failure
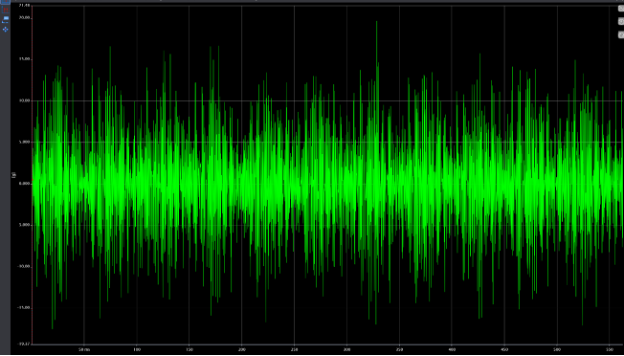
Figure 8: Waveform- Late Stages of Degradation
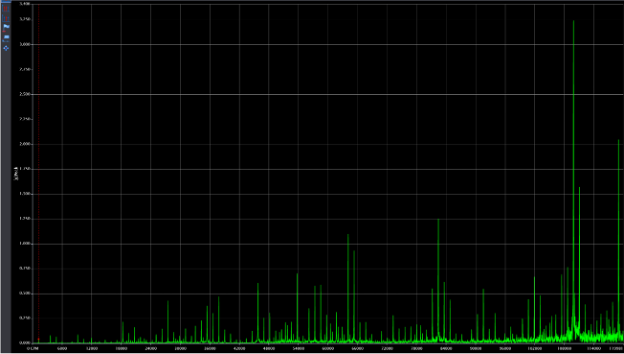
Figure 9: Spectrum- Late Stages of Degradation
The observation noted throughout was that the blower outboard bearing was failing. Failure of this bearing could also translate to damage to the shaft and other blower components if not addressed in a timely manner.
Constant communication between Hydro and the plant prevented the issue from becoming an unexpected and catastrophic failure.
Root Cause Analysis & Remediation:
The data captured by Centaur during the monitoring period was instrumental in conducting a thorough root cause analysis. It provided a comprehensive overview of the conditions leading to the outboard bearing failure, enabling Hydro’s engineers to identify contributing factors, such as operating conditions, lubrication issues, resonance frequencies, and potential misalignments.
 The root cause of the issue was found to be contamination. This PVC unit created a fine dust byproduct that was found in the atmosphere, with large quantities accumulating around the blower units. Over time, the fine PVC dust would penetrate the bearings, compromising the effectiveness of the lubrication and reducing the tolerance inside of the bearings. Plans for remediation included relocating the machines or redesigning the bearing and housing to eliminate the possibility of contamination. The plant ultimately decided relocation was not an option and consulted the bearing manufacturer for an improved design that included a sealed housing.
The root cause of the issue was found to be contamination. This PVC unit created a fine dust byproduct that was found in the atmosphere, with large quantities accumulating around the blower units. Over time, the fine PVC dust would penetrate the bearings, compromising the effectiveness of the lubrication and reducing the tolerance inside of the bearings. Plans for remediation included relocating the machines or redesigning the bearing and housing to eliminate the possibility of contamination. The plant ultimately decided relocation was not an option and consulted the bearing manufacturer for an improved design that included a sealed housing.
Hydro continues to monitor these units, with ongoing reviews of the oil quality, level, and possibility of contamination from moisture, metal, or other sources. In parallel, Hydro also recommended reviewing the load handled by this blower and the rated load of the specified bearings, as improper loading may contribute to premature bearing failure.
Results: Cutting Edge Tech and Real-Time Support
Centaur proved to be the first line of defense in identifying abnormalities in the blower unit’s performance. Leveraging real-time data analytics, Centaur detected escalating vibration levels and issued timely alerts based on preset alarm thresholds. This early warning system allowed the maintenance team to take proactive measures, and consult with Hydro’s engineers on the data, receiving immediate real-time support thus preventing a catastrophic failure and minimizing the impact on overall operations. The ability to pinpoint the issue before complete failure occurred significantly reduced the downtime and associated costs.
This case underscores the value of proactive maintenance strategies for rotating equipment. With a strong focus on customer needs, experience across brands and applications, and a commitment to innovation, Hydro’s capabilities and culture uniquely aligned with the customer’s goals for improving asset reliability and performance.
Learn more about Centaur and how it can help you reduce the cost of rotating equipment ownership.

 By combining reverse engineered data, analytical tools and engineering expertise, a comprehensive approach can be developed to understand and modify hydraulic performance. This process allows pumping equipment to function exactly as required by the system that it fits within.
By combining reverse engineered data, analytical tools and engineering expertise, a comprehensive approach can be developed to understand and modify hydraulic performance. This process allows pumping equipment to function exactly as required by the system that it fits within.
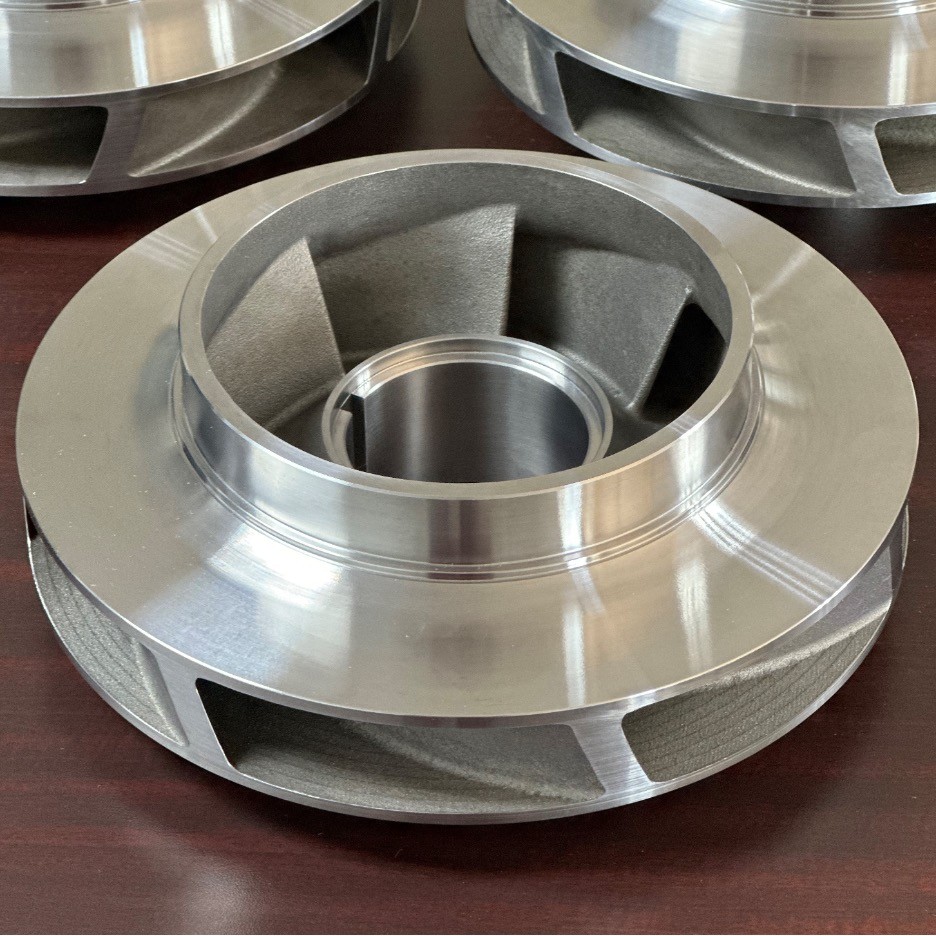

 Hydro Parts Solutions recently manufactured three impellers for a rerate project being developed through Hydro’s Rocky Mountain service center in Denver, CO. Hydro Global Engineering determined the new hydraulic design for the rerated pump, which required modifications to the casing and new impellers.
Hydro Parts Solutions recently manufactured three impellers for a rerate project being developed through Hydro’s Rocky Mountain service center in Denver, CO. Hydro Global Engineering determined the new hydraulic design for the rerated pump, which required modifications to the casing and new impellers.